[2.4] Number of renewable energy sources in campus
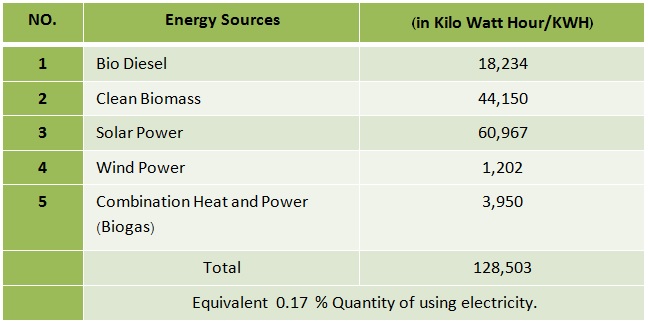
There are 5 kinds of renewable energy which Kasetsart University set a policy for consumption namely: bio diesel, clean biomass, solar power, wind power and combination of heat and power (biogas). The usage of renewable energy is 128,503 kilowatt in 2018.
- Setting of 9 kilowatts solar cell panels for electrical consumption in the university
.
Solar Cell Panels 9 Kilowatts.


ON GRID system
.
Kasetsart University provided an electrical production from solar cell set for demonstration.


Solar Cell Panels 30 Kilowatts.
Figure 2.4-1 Solar Power


Using of solar power for water pump.


Solar energy recycle training station Solar energy fills oxygen in water.
Figure 2.4-1(Cont.) Solar Power
Kasetsart University is keeping update and improves the landscape along the Rapee Sakrik Building. The university choose to provide the pathways light with solar power for energy saving.


Solar cell lamps along the Rapee Sakrik Building.


Figure 2.4-1(Conts.) Solar Power
On 28 March 2018, the 600 upgraded version of ‘Mobike’- smart bicycles were added for service. The bikes were recreated with stronger and wearable structure, adjustable seat, and chargeable solar cell electricity for GPS and unlock system.



Figure 2.4-1 (Conts). The latest new version of Mobike for public transport within Bangkhen campus chargeable solar cell electricity for GPS and unlock system.
- Biodiesel production station


Sustainable development and sustainable growth
Kasetsart University produced biodiesel by BTC-150 machine. The BTC-150 has a capacity of 150 liters/ time and develops consecutively to KUB-200 which has a capacity of 200 liters / time, with a capacity of 700 liters / day.


BTC-150 KUB-200
A 12 hp. & 5-kw.- farm generator powered by integrated fuels of biogas, synthesized gas and diesel oil



A 100-kw.- farm generator powered by integrated fuels of synthesized gas from a 3-stage and diesel oil gasifier powered by fuel of paddy husk and diesel oil compressed bar charcoal on process of production



Biogas production station
Biogas production station of Kasetsart University produced gas from food waste 400 kg. /day and converted into heat energy from a gas tank of 15 cubic meters to use in the canteen.


Dry broiler manure 4 tons/year Dry manure from 6,500 layer chicken yield 20 tons/year Utilization 12 tons of manure was put into grass plot. 8 tons of manure was put into biogas pit.
Poultry manure is put into biogas production dome. The biogas is used for electricity generating system of poultry farm. It is also transformed to fertilizer pellet.
.
7 tons of pig excrement are processed into 12,000 liters of liquid fertilizer for cultivation. It is used 1.5 liters per rai /crop for 8,000 rai of paddy field and 3.5 liters per 3,400 rai of cassava.
Swine manure is put into digester tunnel to produce biogas for in-farm cooking and herbal sauna.
.
Dairy cattle manure is put into digester tunnel to produce the biogas for in-farm cooking and pasteurized-milk production.
.
Cattle manure is put into covered digester pit to produce the biogas for farm electricity. It saves electricity cost of the farm.
- Producing hot gas with a Gasification Stove
Gasification Stove has a diagram of Figure 1, which is heated to the neck at about 1200 ° C. This hot gas is heated to about 5,000 kilojoules (kJ)., which can be ignited. The composition of the biomass consists of Carbon Monoxide 18-25%, Carbon Dioxide 5-10%, Hydrogen 13-15%, Methane 3-5%, Nitrogen 45-54%, and Steam 10-15%. There is also a hot gas fired furnace with charcoal and biomass as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig 2.


Picture 1 Diagram of Gasification Stove Source: Waste to Energy Ltd. Picture 2 gasifier stove with charcoal fuel
5. Usage of wind power




