Waste (WS)
Toxic Waste Handled
Test procedures in laboratory produce many waste. Wastes from operation are risk factors that must be managed systematically. To prevent chemical spills and spread into the environment outside the laboratory by waste management as follows:
- Waste separation
- Collection and restore
- Treatment and elimination
1 Category of waste separation
Wastes from laboratory are easy to dispose, safer and cost of disposal reducing. There is no single waste disposal method suitable for all types of wastes. Therefore, categorization of waste makes it possible to choose the right way for disposal. The categorization should separate general, dangerous and not dangerous waste from each other. Two dangerous qualification of chemical substance should be considered as follows: firstly, prominent characters are flaming, explosion and oxidation. Secondly, inferior characters are toxicity, corrosive, infectious and radioactive. Chemical safety information should be studied from these two type of chemical substance characters.
Example of toxic waste categorization as follows: (Information from Kamphaeng Saen Campus)
Group 1 Solid waste 63,773.08 Kilograms/year
Group 2 Liquid waste 43,994.41 liters/year
Group 3 Radioactive and infectious waste 66,213.90 Kilograms/year
Group 4 Other non-specific waste 20.6 liters/year
Two type of wastes:
- General waste i.e. light bulb, battery and electronic appliances
- Dangerous waste (subjects from laboratory) i.e. solid type; test tubeand reagent bottle, liquid type; chemical and acid solution
2 Waste separation and stowage
It is advisable to separate and keep chemical waste in a waste storage room or specific cabinet in order to be safe. If a container leaks, it may causes severe reaction. A large quantity of toxic gas will cause a fire or explosion. Even if the containers are separated, some chemical waste should not place closely. In addition, compatibility of chemical solution also are considered. Here are some examples:
Process of toxic waste collection (Information from Kamphaeng Saen Campus)
- Chemical substances classification

- Chemical solution grouping
– In case of mixture, grouping by a type of substance that is most proportional.
– Heavy metal substance is on Group 4, regardless of the proportion of all substances.
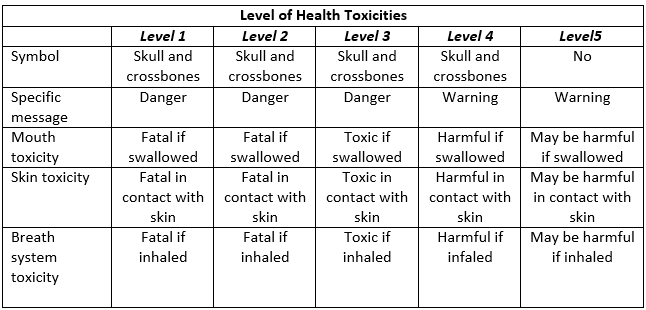
– High toxic substance is in Group 5, regardless of the proportion of all substances and is on level 3 of health hazard criteria or above. Labeling is on a bottle as follows:
- In case unable to group, fills in a list of chemical solution inside a bottle. Volume is shown in percentage or ml. on a label and wait for grouping later.
3 Waste treatment and disposal
Laboratory should have a preliminary management process before disposal as follows:
- Waste treatment before discard: least hazardous waste that can be disposed before released into sanitary system.
- Pre-treatment before disposal waste: hazardous wastes that cannot be eliminated by laboratory, will be treated before send to dispose by waste management company. To reduce danger of storage and transportation.
- Volume reducing before discard: laboratory has a management approach to pre-waste generation. To reduce the amount of wasted on destination. For example, using of non-dangerous chemicals replacing dangerous chemicals and/or reducing of chemical volume that make reaction.
- 4. Reducing of volume before disposal: reducing of disposal budget by decrease volume of waste before sending to waste management
- 3Rs of waste management as follows:
– Reuse : recycling of waste by cleaning and maintenance without changing form of waste.
– Recovery : changing form of waste by detachment, separation and transform process and bring to use again, without original purpose.
– Recycle : reusing of material by transform process. It has different physical and functional but chemical composition as it was.



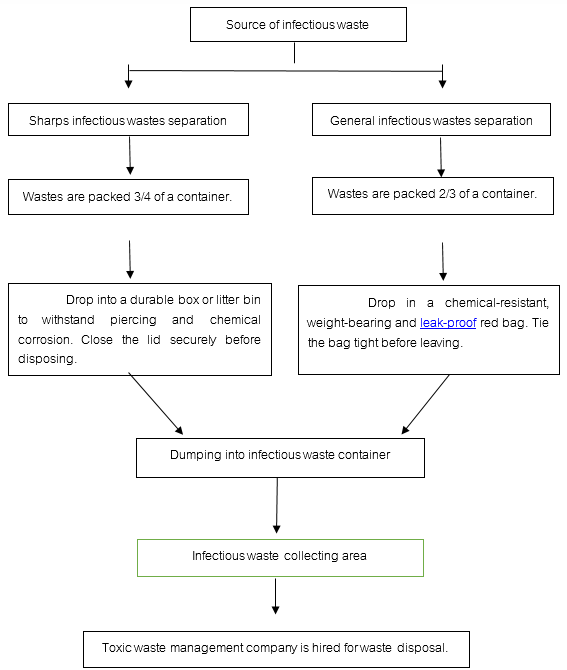
Flowchart of Biohazard Waste Disposal